在Substance当中使用Unity的Shading模型
在PBR的游戏资源制作中,最常用的贴图绘制工具就是Substance Painter。
一般的流程是在SP当中绘制到模型贴图然后在导入到unity当中。
在这个过程中美术会遇到很严重的效果不匹配的问题,在Unity中效果不理想就需要返回SP当中重新调整。因为SP的光照模型和Unity的光照模型不同,尤其是在Unity升级了HDRP以后光照计算再次出现了变化。为了能够让贴图绘制人员能够在SP和Unity当中看到的效果一致,我们需要重写SP的光照计算Shader。
SP提供了这个功能,参考的文件夹位于:
Substance Painter\resources\shelf\allegorithmic\shaders
这个目录下面有很多glsl文件,语法使用glsl语法,能够控制的部分类似于Unity Legac的Surface Shader。
下面是我实现的SPShader,使用了和Unity一样的光照模型,支持Substance Painter 2019.1.0:
//- Allegorithmic Metal/Rough PBR shader
//- ====================================
//-
//- Import from libraries.
import lib-sss.glsl
import lib-pbr.glsl
import lib-emissive.glsl
import lib-pom.glsl
import lib-utils.glsl
//- Declare the iray mdl material to use with this shader.
//: metadata {
//: "mdl":"mdl::alg::materials::skin_metallic_roughness::skin_metallic_roughness"
//: }
//- Channels needed for metal/rough workflow are bound here.
//: param auto channel_basecolor
uniform SamplerSparse basecolor_tex;
//: param auto channel_roughness
uniform SamplerSparse roughness_tex;
//: param auto channel_metallic
uniform SamplerSparse metallic_tex;
//: param auto channel_specularlevel
uniform SamplerSparse specularlevel_tex;
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Constants
#define HALF_MAX 65504.0 // (2 - 2^-10) * 2^15
#define HALF_MAX_MINUS1 65472.0 // (2 - 2^-9) * 2^15
#define EPSILON 1.0e-4
#define PI 3.14159265359
#define TWO_PI 6.28318530718
#define FOUR_PI 12.56637061436
#define INV_PI 0.31830988618
#define INV_TWO_PI 0.15915494309
#define INV_FOUR_PI 0.07957747155
#define HALF_PI 1.57079632679
#define INV_HALF_PI 0.636619772367
#define FLT_EPSILON 1.192092896e-07 // Smallest positive number, such that 1.0 + FLT_EPSILON != 1.0
#define FLT_MIN 1.175494351e-38 // Minimum representable positive floating-point number
#define FLT_MAX 3.402823466e+38 // Maximum representable floating-point number
#define DEFAULT_SPECULAR_VALUE 0.04
#define FLT_INF asfloat(0x7F800000)
#define FLT_EPS 5.960464478e-8 // 2^-24, machine epsilon: 1 + EPS = 1 (half of the ULP for 1.0f)
#define HALF_MIN 6.103515625e-5 // 2^-14, the same value for 10, 11 and 16-bit: https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Small_Float_Formats
#define HALF_MAX 65504.0
#define UINT_MAX 0xFFFFFFFFu
// HDRP模拟光源
//: param custom { "default": [10.0, 10.0, 10.0], "label": "Light Direction", "min": -20, "max": 20 }
uniform vec3 lightDir;
//: param custom { "default": 1.0, "label": "Light Color", "widget": "color" }
uniform vec3 lightColor;
//: param custom { "default": 1.0, "label": "Diffuse Dimmer", "min": 0.0, "max": 32.0 }
uniform float diffuseDimmer;
//: param custom { "default": 1.0, "label": "Specular Dimmer", "min": 0.0, "max": 32.0 }
uniform float specularDimmer;
//: param custom { "default": 1.0, "label": "Lihgt Intensity", "min": 0.0, "max": 32.0 }
uniform float lightIntensity;
struct DirectLighting
{
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
};
float F_Schlick(float f0, float f90, float u)
{
float x = 1.0 - u;
float x2 = x * x;
float x5 = x * x2 * x2;
return (f90 - f0) * x5 + f0; // sub mul mul mul sub mad
}
float F_Schlick(float f0, float u)
{
return F_Schlick(f0, 1.0, u); // sub mul mul mul sub mad
}
vec3 F_Schlick(vec3 f0, float f90, float u)
{
float x = 1.0 - u;
float x2 = x * x;
float x5 = x * x2 * x2;
return f0 * (1.0 - x5) + (f90 * x5); // sub mul mul mul sub mul mad*3
}
vec3 F_Schlick(vec3 f0, float u)
{
return F_Schlick(f0, 1.0, u); // sub mul mul mul sub mad*3
}
float DV_SmithJointGGX(float NdotH, float NdotL, float NdotV, float roughness, float partLambdaV)
{
float a2 = (roughness * roughness);
float s = (NdotH * a2 - NdotH) * NdotH + 1.0;
float lambdaV = NdotL * partLambdaV;
float lambdaL = NdotV * sqrt((-NdotL * a2 + NdotL) * NdotL + a2);
vec2 D = vec2(a2, s * s); // Fraction without the multiplier (1/Pi)
vec2 G = vec2(1, lambdaV + lambdaL); // Fraction without the multiplier (1/2)
// This function is only used for direct lighting.
// If roughness is 0, the probability of hitting a punctual or directional light is also 0.
// Therefore, we return 0. The most efficient way to do it is with a max().
return INV_PI * 0.5 * (D.x * G.x) / max(D.y * G.y, FLT_MIN);
}
float DisneyDiffuseNoPI(float NdotV, float NdotL, float LdotV, float perceptualRoughness)
{
// (2 * LdotH * LdotH) = 1 + LdotV
// float fd90 = 0.5 + 2 * LdotH * LdotH * perceptualRoughness;
float fd90 = 0.5 + (perceptualRoughness + perceptualRoughness * LdotV);
// Two schlick fresnel term
float lightScatter = F_Schlick(1.0, fd90, NdotL);
float viewScatter = F_Schlick(1.0, fd90, NdotV);
// Normalize the BRDF for polar view angles of up to (Pi/4).
// We use the worst case of (roughness = albedo = 1), and, for each view angle,
// integrate (brdf * cos(theta_light)) over all light directions.
// The resulting value is for (theta_view = 0), which is actually a little bit larger
// than the value of the integral for (theta_view = Pi/4).
// Hopefully, the compiler folds the constant together with (1/Pi).
return (1 / 1.03571) * (lightScatter * viewScatter);
}
float DisneyDiffuse(float NdotV, float NdotL, float LdotV, float perceptualRoughness)
{
return INV_PI * DisneyDiffuseNoPI(NdotV, NdotL, LdotV, perceptualRoughness);
}
float GetSmithJointGGXPartLambdaV(float NdotV, float roughness)
{
float a2 = (roughness * roughness);
return sqrt((-NdotV * a2 + NdotV) * NdotV + a2);
}
void BSDF( vec3 V,
vec3 L,
float NdotL,
float unclampNdotV,
vec3 fresnel0,
float roughness,
float perceptualRoughness,
out vec3 diffuseLighting,
out vec3 specularLighting)
{
float LdotV, NdotH, LdotH, NdotV, invLenLV;
LdotV = dot(L, V);
invLenLV = inversesqrt(max(2.0 * LdotV + 2.0, FLT_EPS));
NdotH = clamp((NdotL + unclampNdotV) * invLenLV,0,1);
LdotH = clamp(invLenLV * LdotV + invLenLV,0,1);
NdotV = max(unclampNdotV, 0.0001);
vec3 F = F_Schlick(fresnel0, LdotH);
float partLambdaV = GetSmithJointGGXPartLambdaV(NdotV, roughness);
float DV = DV_SmithJointGGX(NdotH, NdotL, NdotV, roughness, partLambdaV);
specularLighting = F * DV;
//float diffuseTerm = Lambert();
float diffuseTerm = DisneyDiffuse(NdotV, NdotL, LdotV, perceptualRoughness);
diffuseLighting = vec3(diffuseTerm,diffuseTerm,diffuseTerm);
}
DirectLighting ShadeSurface_Directional(vec3 baseColor,
float roughness,
float metallic,
vec3 fresnel0,
vec3 N,
vec3 V)
{
DirectLighting lighting;
//ZERO_INITIALIZE(DirectLighting, lighting);
vec3 L = normalize(lightDir); // 光线方向
vec3 color = lightIntensity *lightColor;
float NdotL = dot(N, L); // Do not saturate
float NdotV = dot(N, V);
vec3 diffuseBsdf, specularBsdf;
BSDF(V, L, NdotL, NdotV, fresnel0, roughness*roughness, roughness,diffuseBsdf, specularBsdf);
float intensity = max(NdotL,0);
lighting.diffuse = diffuseBsdf * (intensity * diffuseDimmer);
lighting.specular = specularBsdf * (intensity * specularDimmer);
lighting.diffuse *= color * baseColor;
lighting.specular *= color * baseColor;
return lighting;
}
vec3 ComputeFresnel0(vec3 baseColor, float metallic, float dielectricF0)
{
return mix(vec3(dielectricF0,dielectricF0,dielectricF0), baseColor, metallic);
}
//- Shader entry point.
void shade(V2F inputs)
{
// Apply parallax occlusion mapping if possible
vec3 viewTS = worldSpaceToTangentSpace(getEyeVec(inputs.position), inputs);
applyParallaxOffset(inputs, viewTS);
// Fetch material parameters, and conversion to the specular/roughness model
float roughness = getRoughness(roughness_tex, inputs.sparse_coord);
vec3 baseColor = getBaseColor(basecolor_tex, inputs.sparse_coord);
float metallic = getMetallic(metallic_tex, inputs.sparse_coord);
float specularLevel = getSpecularLevel(specularlevel_tex, inputs.sparse_coord);
vec3 diffColor = generateDiffuseColor(baseColor, metallic);
vec3 specColor = generateSpecularColor(specularLevel, baseColor, metallic);
float occlusion = getAO(inputs.sparse_coord) * getShadowFactor();
float specOcclusion = specularOcclusionCorrection(occlusion, metallic, roughness);
LocalVectors vectors = computeLocalFrame(inputs);
vec3 fresnel0 = ComputeFresnel0(baseColor, metallic, DEFAULT_SPECULAR_VALUE);
//HDRP光照计算部分
DirectLighting lighting = ShadeSurface_Directional( baseColor,
roughness,
metallic,
fresnel0,
vectors.normal,
vectors.eye);
// Feed parameters for a physically based BRDF integration
//emissiveColorOutput(pbrComputeEmissive(emissive_tex, inputs.sparse_coord));
//albedoOutput(diffColor);
//diffuseShadingOutput(occlusion * envIrradiance(vectors.normal));
diffuseShadingOutput(lighting.diffuse * getShadowFactor());
specularShadingOutput(lighting.specular * getShadowFactor());
//sssCoefficientsOutput(getSSSCoefficients(inputs.sparse_coord));
}
上面的是SP的glslShader。为了能够更好的理解Unity HDRP的光照模型,我用unity的格式写了一个直线光计算的Shader,提取自Lit.Shader代码。下面的文件是Unity的hlsl语法Shader,比较重要的部分就是bsdf函数,可以直接放在HDRP5.10.0版本以上使用:
Shader "Unlit/SubstacnePainter"
{
Properties
{
baseColor ("baseColor", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
roughness ("roughness", Range(0,1)) = 1
metallic ("metallic", Range(0,1)) = 1
diffuseDimmer ("diffuseDimmer", Float) = 1
specularDimmer ("specularDimmer", Float) = 1
lightColor ("lightColor", Color) = (1,1,1,1)
lightIntensity ("lightIntensity", Float) = 1
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float3 normal : NORMAL;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
float3 worldPos : TEXCOORD1;
float3 worldNormal : TEXCOORD2;
};
float4 baseColor;
float4 lightColor;
float roughness;
float metallic;
uniform float diffuseDimmer;
uniform float specularDimmer;
uniform float3 lightDir;
uniform float lightIntensity;
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.core/ShaderLibrary/Common.hlsl"
#include "Packages/com.unity.render-pipelines.high-definition/Runtime/ShaderLibrary/ShaderVariables.hlsl"
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Constants
#define HALF_MAX 65504.0 // (2 - 2^-10) * 2^15
#define HALF_MAX_MINUS1 65472.0 // (2 - 2^-9) * 2^15
#define EPSILON 1.0e-4
#define PI 3.14159265359
#define TWO_PI 6.28318530718
#define FOUR_PI 12.56637061436
#define INV_PI 0.31830988618
#define INV_TWO_PI 0.15915494309
#define INV_FOUR_PI 0.07957747155
#define HALF_PI 1.57079632679
#define INV_HALF_PI 0.636619772367
#define FLT_EPSILON 1.192092896e-07 // Smallest positive number, such that 1.0 + FLT_EPSILON != 1.0
#define FLT_MIN 1.175494351e-38 // Minimum representable positive floating-point number
#define FLT_MAX 3.402823466e+38 // Maximum representable floating-point number
#define DEFAULT_SPECULAR_VALUE 0.04
#define FLT_INF asfloat(0x7F800000)
#define FLT_EPS 5.960464478e-8 // 2^-24, machine epsilon: 1 + EPS = 1 (half of the ULP for 1.0f)
#define HALF_MIN 6.103515625e-5 // 2^-14, the same value for 10, 11 and 16-bit: https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/Small_Float_Formats
#define HALF_MAX 65504.0
#define UINT_MAX 0xFFFFFFFFu
// HDRP模拟光源
struct DirectLighting
{
float3 diffuse;
float3 specular;
};
float F_Schlick(float f0, float f90, float u)
{
float x = 1.0 - u;
float x2 = x * x;
float x5 = x * x2 * x2;
return (f90 - f0) * x5 + f0; // sub mul mul mul sub mad
}
float F_Schlick(float f0, float u)
{
return F_Schlick(f0, 1.0, u); // sub mul mul mul sub mad
}
float3 F_Schlick(float3 f0, float f90, float u)
{
float x = 1.0 - u;
float x2 = x * x;
float x5 = x * x2 * x2;
return f0 * (1.0 - x5) + (f90 * x5); // sub mul mul mul sub mul mad*3
}
float3 F_Schlick(float3 f0, float u)
{
return F_Schlick(f0, 1.0, u); // sub mul mul mul sub mad*3
}
float3 ComputeFresnel0(float3 baseColor, float metallic, float dielectricF0)
{
return lerp(dielectricF0.xxx, baseColor, metallic);
}
float DV_SmithJointGGX(float NdotH, float NdotL, float NdotV, float roughness, float partLambdaV)
{
float a2 = (roughness * roughness);
float s = (NdotH * a2 - NdotH) * NdotH + 1.0;
float lambdaV = NdotL * partLambdaV;
float lambdaL = NdotV * sqrt((-NdotL * a2 + NdotL) * NdotL + a2);
float2 D = float2(a2, s * s); // Fraction without the multiplier (1/Pi)
float2 G = float2(1, lambdaV + lambdaL); // Fraction without the multiplier (1/2)
// This function is only used for direct lighting.
// If roughness is 0, the probability of hitting a punctual or directional light is also 0.
// Therefore, we return 0. The most efficient way to do it is with a max().
return INV_PI * 0.5 * (D.x * G.x) / max(D.y * G.y, FLT_MIN);
}
float DisneyDiffuseNoPI(float NdotV, float NdotL, float LdotV, float perceptualRoughness)
{
// (2 * LdotH * LdotH) = 1 + LdotV
// float fd90 = 0.5 + 2 * LdotH * LdotH * perceptualRoughness;
float fd90 = 0.5 + (perceptualRoughness + perceptualRoughness * LdotV);
// Two schlick fresnel term
float lightScatter = F_Schlick(1.0, fd90, NdotL);
float viewScatter = F_Schlick(1.0, fd90, NdotV);
// Normalize the BRDF for polar view angles of up to (Pi/4).
// We use the worst case of (roughness = albedo = 1), and, for each view angle,
// integrate (brdf * cos(theta_light)) over all light directions.
// The resulting value is for (theta_view = 0), which is actually a little bit larger
// than the value of the integral for (theta_view = Pi/4).
// Hopefully, the compiler folds the constant together with (1/Pi).
return (1 / 1.03571) * (lightScatter * viewScatter);
}
float DisneyDiffuse(float NdotV, float NdotL, float LdotV, float perceptualRoughness)
{
return INV_PI * DisneyDiffuseNoPI(NdotV, NdotL, LdotV, perceptualRoughness);
}
float GetSmithJointGGXPartLambdaV(float NdotV, float roughness)
{
float a2 = (roughness * roughness);
return sqrt((-NdotV * a2 + NdotV) * NdotV + a2);
}
void BSDF( float3 V,
float3 L,
float NdotL,
float unclampNdotV,
float3 fresnel0,
float roughness,
float perceptualRoughness,
out float3 diffuseLighting,
out float3 specularLighting)
{
float LdotV, NdotH, LdotH, NdotV, invLenLV;
/*
GetBSDFAngle(V, L, NdotL, preLightData.NdotV, LdotV, NdotH, LdotH, NdotV, invLenLV);
*/
LdotV = dot(L, V);
invLenLV = rsqrt(max(2.0 * LdotV + 2.0, FLT_EPS));
NdotH = clamp((NdotL + unclampNdotV) * invLenLV, 0, 1);
LdotH = clamp(invLenLV * LdotV + invLenLV, 0, 1);
NdotV = max(unclampNdotV, 0.0001);
float3 F = F_Schlick(fresnel0, LdotH);
/*
计算彩虹色
if (HasFlag(bsdfData.materialFeatures, MATERIALFEATUREFLAGS_LIT_IRIDESCENCE))
{
F = lerp(F, bsdfData.fresnel0, bsdfData.iridescenceMask);
}
*/
float partLambdaV = GetSmithJointGGXPartLambdaV(NdotV, roughness);
float DV = DV_SmithJointGGX(NdotH, NdotL, NdotV, roughness, partLambdaV);
specularLighting = F * DV;
//float diffuseTerm = Lambert();
float diffuseTerm = DisneyDiffuse(NdotV, NdotL, LdotV, perceptualRoughness);
diffuseLighting = float3(diffuseTerm,diffuseTerm,diffuseTerm);
}
DirectLighting ShadeSurface_Directional(float3 baseColor,
float roughness,
float metallic,
float3 fresnel0,
float3 N,
float3 V)
{
DirectLighting lighting;
//ZERO_INITIALIZE(DirectLighting, lighting);
float3 L = normalize(-lightDir); // 光线方向
float3 color = lightIntensity * lightColor;
float NdotL = dot(N, L); // Do not saturate
float NdotV = dot(N, V);
/*
计算阴影和光照衰减
float attenuation;
EvaluateLight_Directional(lightLoopContext, posInput, light, builtinData, N, L, NdotL, color, attenuation);
*/
//ClampRoughness(roughness, light.minRoughness);
roughness = max(roughness, 0.001225);
float3 diffuseBsdf, specularBsdf;
BSDF(V, L, NdotL, NdotV, fresnel0, roughness*roughness, roughness,diffuseBsdf, specularBsdf);
/*
计算反射透射
bool surfaceReflection = NdotL > 0;
if (surfaceReflection)
{
*/
// so there NdotL must be bigger than 0
float intensity = saturate(NdotL);
lighting.diffuse = diffuseBsdf * (intensity * diffuseDimmer);
lighting.specular = specularBsdf * (intensity * specularDimmer);
lighting.diffuse *= color * baseColor;
lighting.specular *= color * baseColor;
/*
计算透射
}
else if (MaterialSupportsTransmission(bsdfData))
{
// Apply wrapped lighting to better handle thin objects at grazing angles.
float wrapNdotL = ComputeWrappedDiffuseLighting(NdotL, TRANSMISSION_WRAP_LIGHT);
float intensity = attenuation * wrapNdotL;
// We use diffuse lighting for accumulation since it is going to be blurred during the SSS pass.
// Note: Disney's LdoV term in 'diffuseBsdf' does not hold a meaningful value
// in the context of transmission, but we keep it unaltered for performance reasons.
lighting.diffuse = transmittance * (diffuseBsdf * (intensity * light.diffuseDimmer));
lighting.specular = 0; // No spec trans, the compiler should optimize
}
*/
return lighting;
}
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = mul(UNITY_MATRIX_VP,mul(UNITY_MATRIX_M,v.vertex));
o.worldPos = GetAbsolutePositionWS(mul(UNITY_MATRIX_M, v.vertex));
o.worldNormal = TransformObjectToWorldNormal(v.normal);
o.uv = v.uv;
return o;
}
float4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
float3 fresnel0 = ComputeFresnel0(baseColor, metallic, DEFAULT_SPECULAR_VALUE);
float3 V = normalize(_WorldSpaceCameraPos.xyz - i.worldPos);
float3 N = normalize(i.worldNormal);
//HDRP光照计算部分
DirectLighting lighting = ShadeSurface_Directional( baseColor,
roughness,
metallic,
fresnel0,
N,
V);
return float4(lighting.diffuse.xyz + lighting.specular.xyz,1);
}
ENDHLSL
}
}
}
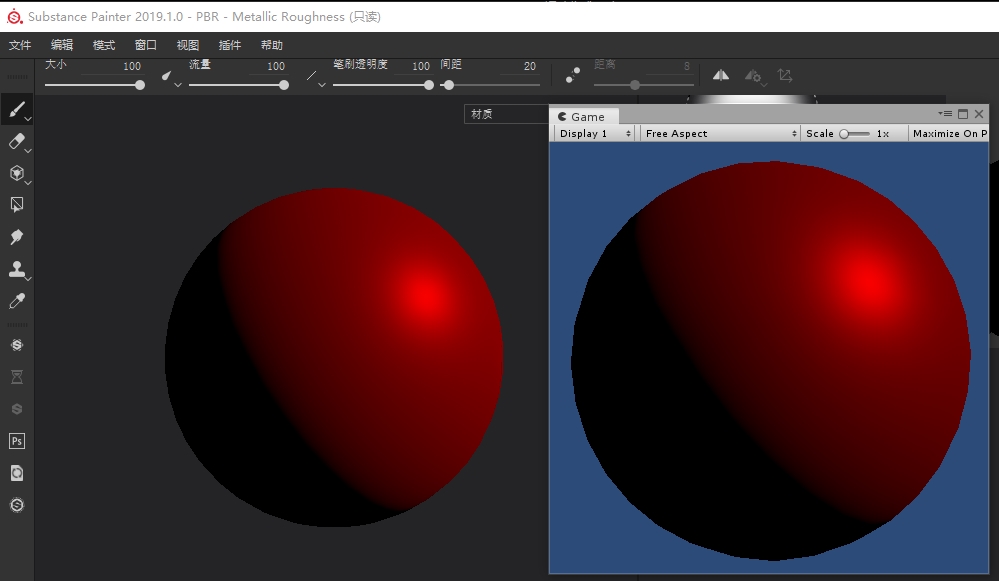
下面就是Unity和SubstancePainter的光照结果对比。